4.0 Solar photovoltaics

Solar revolution: Evolution of photovoltaic technology in the 21st century
In the previous article, we discussed the first-stage evolution of photovoltaic technology. It was the biography of photovoltaic technology before the beginning of the 21st century.
What happened in the 21st century?
Latest trends in solar photovoltaic technology
It is interesting to know that the worldwide cumulative photovoltaic capacity merely stood at about 95 kW in 1968. It took almost three decades to reach 950 MW in 1998. The cumulative worldwide installation had been growing at a snail’s pace until about 2000 and reached a milestone of 1000 MW in 1999 [2]. Showing a green light for a greener world, the cumulative capacity which was about 8 GW in 2007, nearly doubled to hit 15 GW of capacity in 2008 [3]. Since then, the capacity started expanding swiftly, as it can be seen in the following table and column chart.
Table 01: Worldwide cumulative and added photovoltaic capacity [3]
|
Year |
2007 |
2008 |
2009 |
2010 |
2011 |
2012 |
2013 |
2014 |
2015 |
2016 |
2017 |
|
Added capacity (GW) |
2.5 |
6.6 |
8 |
17 |
31 |
29 |
38 |
40 |
51 |
76 |
98 |
|
Cumulative capacity (GW) |
8 |
15 |
23 |
40 |
70 |
100 |
137 |
177 |
228 |
303 |
402 |
According to above table, as much as 98 GW of solar photovoltaic capacity has been added in 2017 thereby raising the worldwide cumulative capacity to 402 GW which is now comparable with worldwide cumulative solar hot water capacity. Worldwide cumulative solar hot water capacity has grown by merely 16 GW and reached 472 GW in 2017. This reveals a continuous decline in annual growth whilst solar photovoltaic technology is showing an overwhelming progress. Following bar chart clearly illustrates how fast worldwide cumulative photovoltaic capacity has been growing during the recent past [3].
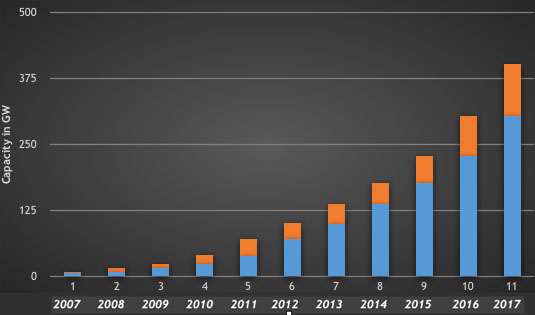
Figure 01: Worldwide cumulative and added photovoltaic capacity [3]
What is behind the boom?
As we can see it, the cumulative photovoltaic capacity has now been growing fast, but it was not until 1998 which seems to be a pivotal point in the photovoltaics’ history. What is behind the sudden increase in worldwide installations?
We can identify a lot of forces attempting to shift the world’s energy interest towards solar photovoltaics. Let us discuss some of the most vigorous forces.
- Cost reduction:
Prior to the beginning of the 21st century, there was a lot of impedance to the commercialization of photovoltaic technology. It was too expensive for commercial implementations compared to fossil fuels and also other renewable energy technologies like hydropower, wind power, and concentrating solar thermal. Price of solar photovoltaic modules has been continuously falling and eventually, photovoltaics became economically viable and competitive with the fossil fuel prices. The continuous drop in the price is what made it the most popular and fastest-growing renewable energy technology in the 21st century. Price is forecast to drop further attracting more and more investments.
- Environmental concerns:
Even in the 1950s, people worried a lot about the possible detrimental effects of climate change. Fossil fuel burning was the main suspect. Not only scientific community, even government bodies and private organizations actively started fighting the climate change leading to many achievements such as the Kyoto protocol in which state parties committed reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The best way to did it was switching to renewable energy sources as soon as possible. Many countries introduced attractive renewable energy policies to promote solar PV and encourage the public to invest in solar PV. Thanks to such government support and falling price of solar PV, investing in solar PV has now become a win-win for each party involved in.
- Increasing price and rapid depletion of fossil fuels:
Our primary sources of energy, fossil fuels are rapidly depleting due to heavy consumption whilst price is increasing. This trend naturally forces to search for potential alternatives. Price of solar PV modules is already competitive with most of the other renewable energy technologies. Increasing price of fossil fuels, and rapid depletion of fossil fuels direct more attention towards photovoltaics.
- Improved efficiency:
Efficiency of solar photovoltaics is being improved day by day. A number of photovoltaic technologies have been developed with different efficiencies. Multi-junction concentrated solar cells offer the highest efficiencies but are too expensive. Single crystalline and polycrystalline silicon solar cells also offer reasonable efficiencies yet still are cost-effective than most of the other types of photovoltaics. Various state of the art technologies (Tandem solar cells, PERC, etc.) have already been employed successfully, leading to more efficient photovoltaics.
These unique features make solar photovoltaics an ideal alternative to depleting fossil fuels. There is now no any other type of renewable energy technology to compete with photovoltaics. In fact, there were several competitors in the past namely hydropower, concentrating solar thermal, and wind power. However, most of the potential hydropower sources are already being exploited and thus hydropower capacity has been reaching a plateau. Furthermore, when capital investment, space-efficiency, environmental impact, payback time, etc. are taken into consideration, photovoltaic technology is more practically viable than concentrating solar thermal, and wind power. It is not a rhapsody. Take a look at the following bar chart. It clearly depicts that solar photovoltaics was the fastest-growing renewable energy technology which added 98 GW of power in 2017. This is nearly twice the capacity added by wind power during the same year. Wind power, hydropower, bio power, and geothermal power have added 52 GW, 19 GW, 8 GW, and 1 GW of power, respectively, in 2017.
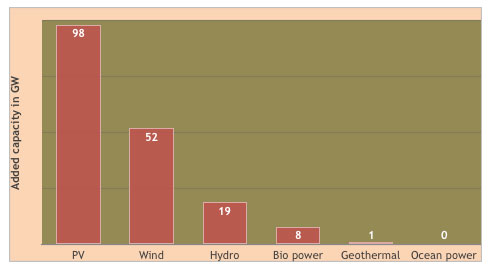
Figure 02: Capacity added by different renewable energy technologies in 2017 [3]
To sum up, photovoltaic technology has evolved to be a commercially viable and technically feasible technology capable of providing an unimaginable amount of energy to meet mankind’s energy demand, making the world greener and sustainable. With continuous research and development, it would continually be evolving and revolutionizing the world with impressive benefits.
It is real!
We are all witnesses!
References
[1] Harmon, C. (2000). Experience curves of photovoltaic technology.
[2] Guha, S. (2005, January). Can your roof provide your electrical needs?-the growth prospect of building-integrated photovoltaic. In Photovoltaic Specialists Conference, 2005. Conference Record of the Thirty-first IEEE (pp. 12-16). IEEE.
[3] REN21. 2018. Renewables 2018 Global Status Report (Paris: REN21 Secretariat).
